Ethical hacking is when someone is allowed to try to get into a computer system, app, or data without permission by using the same methods and techniques that bad people use. This helps find holes in security that can be fixed before a bad person can use them.
Ethical hackers are security experts who do these preventative checks on an organization’s security to make it safer. An ethical hacker’s job is to get permission from the company or owner of an IT asset before they do anything bad.
Ethical hackers are just as skilled and use the same tools and methods as bad hackers. The only difference is that their goal is to make networks safer without hurting the users or the networks themselves.

Ethics-based hacking is a lot like practicing for real hacks in a lot of ways. Businesses hire “ethical hackers” to attack their computer networks in a fake way. The good hackers use these attacks to show how real thieves get into a network and what they can do once they’re there.
The security analysts at the company can use this knowledge to fix holes in security systems, make them stronger, and keep sensitive data safe.
“Ethical hacking” and “penetration testing” are words that are sometimes used to refer to the same thing. However, security tests aren’t the only thing that good hackers do. Ethical hackers can also do other tasks related to information security, such as vulnerability assessments, malware analysis, and more.
Why the Word Hacking is Considered to be Ethical?
There are some of the rules that must have to be followed to get the work in a legal way. Hackers follow four main rules about protocols to remain ethical in this hacking process.
- Keep the law: Get the right permissions before you access and do a security review.
- Describe the scope: Figure out what the evaluation will cover so that the ethical hacker’s work stays legal and within the limits set by the company.
- Tell everyone what you found: Notify the organization of all the security holes that were found during the assessment and give them tips on how to fix them.
- Be careful with sensitive info: Ethical hackers may have to sign a nondisclosure agreement along with other rules set by the group they are working for. This depends on how sensitive the data is.
Why ethical hacking is important?
At the start of international wars, terrorist groups paid cybercriminals to break into security systems, either to threaten national security or to get huge amounts of money by putting malware on them and blocking access. This has led to the steady rise of hacking. Organizations have to keep their hack-protection strategies up to date and add new technologies to protect their systems before they are hacked.
Every day, more bugs, malware, viruses, and ransomware are released. This makes it necessary for ethical hacking services to protect the networks of businesses, government agencies, and the military.
You may also like to Read
Is Crypto30x.com Your Gateway to Easy Crypto Trading?
What are Different Kinds of Ethical Hacking?
It’s not a secret that hackers can get into any system, process, website, gadget, etc. That way, good hackers can imagine how the hack could happen and what damage it might cause. They also need to know the tools and methods that bad hackers are likely to use.
1. Web Application Hacking:
Web applications connect users to web servers through a collection of web pages that are either made on the server end or contain script code that is run dynamically in the client Web browser.
2. System Hacking:
System hacking, also called “cyber hacking,” is when someone gets into a computer system or network without permission.

3. Web Server Hacking:
The computer program that helps send content that can be accessed through the Internet is called a web server. It can also be called the hardware, the computer, or the software. A web server is both the hardware and the software that is placed on a computer. Most people think that a web server is just the hardware. A web server’s main job is to send web pages to clients who ask for them using the Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP).
4. Hacking Wireless Network:
In the current world, wireless networks are becoming more and more common. Most importantly, they changed how people talk and connect with each other. Wi-Fi networks make it easy to join and stay connected in homes and businesses alike. Even though these networks are helpful, they often come with the chance of security threats.
5. Social Engineering:
Social engineering is a way to trick people into giving up private information, access, or goods by taking advantage of mistakes people make. In cybercrime, these “human hacking” scams usually work by tricking users who don’t know what’s going on into giving away data, spreading malware, or getting into systems that aren’t supposed to be accessed. Attacks can happen in person, online, or in some other way.

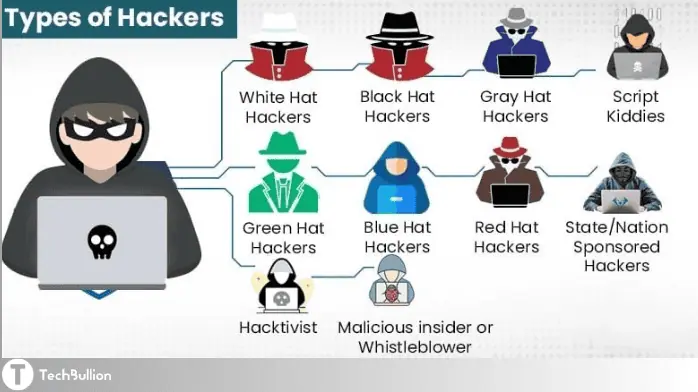
What are Different Kinds of Hackers?
The many varieties of hackers are as follows:
Professional Hackers:
Hackers with a moral compass who utilize their knowledge to help businesses patch security holes. Permission is obtained and legal protocols are followed in their job.
Criminal Hackers:
Hackers with malicious intent who target vulnerable systems or individuals in order to earn financial benefit at the expense of those entities or individuals. What they do is not legal.
Malicious Cyber-Agents:
Computer hackers that don’t necessarily belong to either the white or black hat categories. Although they may do things without authorization, their intentions are typically not hostile, and they frequently disclose vulnerabilities to the public or the company after the fact.
Young Writers:
Those without extensive knowledge of the underlying technology engage in assaults using pre-written scripts or tools.
A group known as hacktivists:
Hackers with a social or political agenda who use their expertise to further those causes. In order to further their cause, they frequently deface websites or leak confidential information.
Hackers funded by states:
Individuals or groups that engage in cyber espionage, cyberwarfare, or surveillance on behalf of foreign governments are known as “hackers.”
Ethical hacking Digital thieves:
Criminal hackers are those that break the law in order to make money, whether by phishing, ransomware attacks, or the theft of credit card details.
Dangers from Within:
People working for a company who illicitly or accidentally use their position to seek personal benefit or commit destructive acts against the company or its data.
Hackers who blow the whistle:
Cybercriminals are people who break into computer systems and reveal confidential information in order to expose wrongdoing within corporations.
Members of the Red Hat Hacker community:
Hackers that actively seek out and disrupt the activities of black hat hackers and cybercriminals are known as vigilante hackers.
Professional Hackers:
Companies hire security experts to check their systems for weaknesses. These individuals are usually considered to be outside experts rather than employees of the company.
Ethical hacking stages:
Ethical hacking is the act of finding holes in a system, program, or an organization’s infrastructure that a hacker could use to take advantage of a person or the organization. They use this method to stop hacks and security holes by breaking the law to get into the systems and look for weak spots. An ethical hacker uses the same methods and way of thinking as a bad hacker to get into an organization’s network and test its tactics.
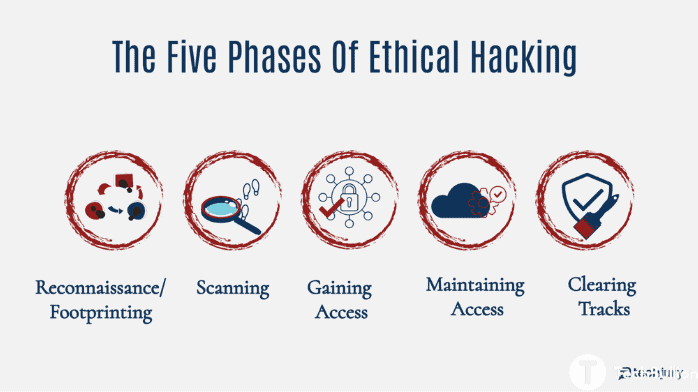
In ethical hacking, there are five stages:
1. Surveying the area:
Conducting research is the initial stage in ethical hacking. Another name for it is “footprinting.” Hackers use active and passive techniques to try to gain various kinds of information, such as domain names, IP addresses, network layouts, and personnel information. The objective is to create a schematic of the target’s physical and digital possessions.
2. Observing in Ethical hacking:
The hacker goes on to scanning once they have collected enough information. It detects active devices, services, and open ports when scanning a network. It also aids in locating potential attack vectors. In most cases, there are three main categories of scanning:
- Examining the Port: Angry IP Scanner and Nmap can detect open ports and services.
- Assessing Security Flaws: System and application vulnerability scanning with Nessus.
- Maps of Networks: Using software like SolarWinds to draw up a plan of the network’s architecture.
3. Entry Procedures:
At this crucial point, the hacker exploits the vulnerabilities discovered during scanning to illicitly access the target machine. This may entail exploiting software, operating systems, or security flaws in the system. From standard user accounts to elevated administrative privileges, we aim to build up entrance at varying degrees of access. Overflows in buffers, SQL injection, and cross-site scripting (XSS) are among ways that attacks can manifest.
4. Maintaining open access:
After breaking into a system, the hacker must remain on the compromised machine in order to steal information or monitor sensitive files. In this way, malicious actors can install backdoors, rootkits, or Trojan horses, which will allow them to access the device even after a restart or patch has been applied. Persistence Methods: Installing malicious software, making anonymous user accounts, and exploiting cron jobs.
5. Removing the trail:
The final component of ethical hacking is maintaining anonymity. To accomplish this, it is necessary to alter timestamps, conceal files, and erase logs in order to eradicate any indication of an assault. The objective is to make it impossible to identify or follow an attacker based on their attacks.
Ethical hackers and penetration testers can utilize the five-step CEH hacking technique to safeguard enterprises from assaults by discovering security gaps, potential entry points, and stopping breaches in security. If you want to know more about how to improve network systems and security rules, you can get a certification in ethical hacking.
Earning the EC-Council Certified Ethical Hacker (CEH v13) credential will teach you the ins and outs of ethical hacking and how to use security tools and techniques to breach a company’s defenses.
Certifications and expertise in ethical hacking:
Ethical hacking certification makes a person eligible to do ethical hacking with consent of a company which is to be tested for security loop holes. A bachelor’s degree is typically required for entry-level positions in ethical hacking, IT security, or a closely related discipline. They are usually well-versed in popular scripting and programming languages, such as SQL and Python.
Certified ethical hacker certification is important in network scanning tools like Nmap, penetration testing platforms like Metasploit, and specialist hacking operating systems like Kali Linux are all within their skill set, and they’re constantly honing it.
Earning credentials is a common way for ethical hackers to show that they are skilled and dedicated to cybersecurity, just like any other professional. Many people get into ethical hacking by taking classes or enrolling in programs that teach you the ropes. Here are a few of the most popular certificates in ethical hacking:
1. Master of Certified Ethical Hacking (CEH):
Among the several ethical hacking credentials offered by the global cybersecurity certification authority EC-Council, CEH stands out.
2. SecureTest+ by CompTIA:
Assessment of vulnerabilities and penetration tests are the main topics of this certification.
3. GPEN, the Sans GIAC Penetration Tester:
Similar to PenTest+, the GPEN certification from the SANS Institute verifies that an ethical hacker is proficient in pen testing.

5 thoughts on “What is Ethical Hacking and Why it Matters in Today’s World?”